|
1 Department of Clinical Chemistry and Pathobiochemistry,
Medical Faculty, University of Technology, Pauwelsstr" D-5100 Aachen,
federal Republic of Germany
2 Department of Immunology, University of Münster, Domagkstr. 3,
D-4400 Münster, Federal Republic of Germany
We have shown previously that tumorspecific T suppressor (Ts) cells
were induced in vivo in BALB/c mice by the syngencic plasmacytoma
(PC) ADJ-PC-5 at very early stages of tumorigenesis [1, 2]. These
Ts cells, which suppress a strong primary cytotoxic T cell response,
have been characterized in detail [1- 3]. There is evidence that
Ts cell-inducing antigens (Ts-Ag) on ADJ-PC-5 plasmacytoma cells
are expressed to some extent on normal BALB/c spleen cells and are
therefore "self' antigens rather than tumor-specific neoantigens
[4]. These data were subsequently confirmed by independent comparable
studies using the EL4 thymoma ofC57B1/6 mice [5]. Thus, the induction
of Ts cells by tumor-associated self antigens seems to be a more
general rule and might be an important tumor escape mechanism. To
characterize Ts-Ag in more detail we have developed an in vitro
system for the selective induction of tumor-specific Ts cells. Ts
cell function would be masked in the in vitro Ts assay in the presence
of activated cytotoxic T cells, which, like specific cytotoxic T
cell clones, are not susceptible to suppression [2]. Activation
of cytotoxic T cells is prevented by pretreatment of the ADJ-PC-5
stimulator cells with glutardjaldehyd (GA) (Fig. 1). In contrast,
specific Ts cells were activated by this approach which suppress
the
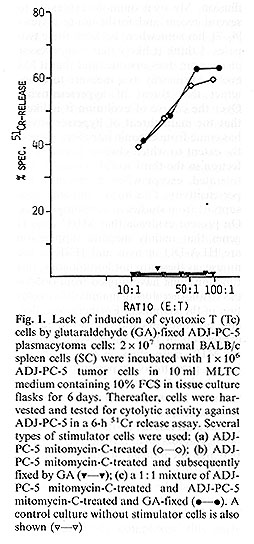
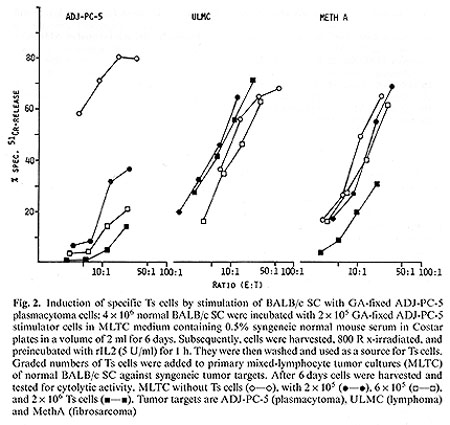
activation of specific cytotoxic T cells in the course of a primary
mixed-lymphocyte tumor cell culture (MLTC) of BALB/c spleen cells
against ADJ-PC-5 plasmacytoma cells, but not against the syngeneic
control tumors ULMC (lymphoma) and MethA (fibrosarcoma) (Fig. 2).
These Ts cells have been further characterized. Even in lectin-kill
assays they have no cytolytic or NK-Iike activity, excluding a veto
effect. In addition, suppression is not due to nonspecific effects
like IL2 consumption, toxic effects by glutaraldehyde or PGE2 release
(data not shown). The phenotype of these Ts cells was Thy 1.2+,
Lyt2.2+, L3T4+, l-Ad-, l-Ed+ as cvidenced by treatment with cytotoxic
monoclonal antibodies and complement. This in vitro system will
be helpful for the isolation and characterization of TsAg, but it
also allows us to study in morc detail the requirements for thc
induction of Ts cells and Ts-cell effector mechanisms.
References
1. Haubeck H-D, Kölsch E (1982) Regulation of immune responses against
the syngeneic AOJ-PC-5 plasmacytoma in BALB/c mice. I II. Induction
of specific T suppressor cells to the BALB/c plasmacytoma ADJ-PC-5
during early stages of tumorigenesis. Immunology 47:503- 509
2. Haubcck H-O, Kölsch E (1986) Regulatioll of immune responses
against the syngeneic AOJ-PC-5 plasmacytoma in BALB/c mice IV. Tumor-specific
T suppressor cells, induced at early stages of tumorigenesis, act
on the induction phase of the tumorspecific cytotoxic T cell response.
Immunobiology 171:357-363
3. Haubeck H-O, Kölsch E (1985) Isolation and characterization of
in vitro and in vivo functions of a tumor-specific T suppressor
cell clone from a BALB/c mouse bearing the syngeneic AOJ-PC-5 plasmacytoma.
J Immunol I35.4297-4302
4. Kloke 0, Haubcck H-O, Kölsch E (1986) Evidence for a T suppressor
cell-inducing antigenic determinant shared by ADJ-PC-5 plasmacytoma
and syngeneic BALB/c spleen cells. Eur J lmmunol 16:659-664
5. Grooten J Leroux-Roels G, Fiers W (1987) Specific suppression
elicited by EL4 lymphoma cells in syngeneic mice. Specifity includes
self-antigens. Eur J lmmunol 17:605
|

