|
1 Department of Molecular Biology and Virus Laboratory.
Wendell M. Stanley Hall. Berkeley. California 94720, USA
2 Department of Zoology, University of California, Berkeley. California
94720. USA
3 Department of Microbiology. University of Southern California.
Los Angeles. California 90033, USA
Abstract
The RNA species of the defective avian acute leukemia virus MC29
and of the defective avian carcinoma virus MH2 and of their helper
viruses were analyzed using gel electrophoresis, fingerprinting
of RNase T 1-resistant oligonucleotides, RNA-cDNA hybridization
and in vitro translation. A 28S RNA species. of 5700 nucleotides,
was identified as MC29- or MH2-specific. MC29 RNA shared 4 out of
about 17 and MH2 RNA at least lout of 16 T1oligonucleotides with
several other avain tumor virus RNAs. In addition MC29 and MH2 RNAs
shared 2 oligonucleotides which were not found in any other viral
RNA tested. 60% of each 28S RNA could be hybridized by DNA complementary
to other avian tumor virus RNAs (group-specific) but 40% could only
be hybridized by homologous cDNA (specific). Src generelated sequences
of Rous sarcoma virus were not found in MC29 or MH2 RNA. The specific
and group-specific sequences of MC29, defined in terms of their
T l-o1igon ucleotides, were located on a map of all T 1-oligonucleotides
of viral RNA. Specific sequences mapped between 0,4 and 0.7 map
units from the 3' poly(A) end and group-specific sequences mapped
between 0 and 0,4 and 0,7 and 1 map units. The MC29-specific RNA
segment was represented by 6 oligonucleotides, two of which were
those shared only by MC29 and MH2 RNAs. In vitro translation of
MC29 RNA generated a major 120000 dalton protein and minor 56000
and 37000 dalton proteins. The 120000 dalton protein shared sequences
with the proteins of the avian tumor viral gag gene, which maps
at the 5' end of independently replicating viruses. Since a gag
gene-related oligonucleotide was also found near the 5' end of MC29
RNA, we propose that the 120000 MC29 protein was translated from
the 5' 60% of MC29 RNA. It would then include sequences of the defective
gag gene as well as MC29-specific sequences. Since both MC29 and
MH2 lack the src (sarcoma) gene of Rous sarcoma virus. it is concluded
that they contain a distinct class of transforming (onc) genes.
We propose that the specific sequences of MC29 and MH2 represent
all. or part of their onc genes because the onc genes of MC29 and
MH2 are specific and represent the only known genetic function of
these viruses. If this proposal is correct. the onc genes of MC29
and MH2 would be related, because the specific RNA sequence of MC29
shares 2 of 6 oligonucleotides with MH2. It would also follow that
the 120000 dalton MC29 protein is a probable onc gene product. because
it is translated from MC29-specific (and group-specific) sequences
and because both MC29- and MH2-transformed cells contain specific
120000 and 100000 dalton proteins. respectively.
Introduction
MC29 and MH2 are avian RNA tumor viruses that cause acute leukemia,
carcinoma and also transform fibroblasts in culture [1,2,3,4,5,6].
This oncogenic cell transformation is due to a transforming gene,
termed onc [7], which has not been defined genetically or biochemically.
Both viruses require a helper virus for replication because they
are defective in all three replicative genes of the avian tumor
virus group gag (for internal group-specific antigen),pol (for DNA
polymerase) and env (envelope glycoprotein) [7]. The viral genome
was identified as a 28S RNA species of 5700 nucleotides because
it is absent from pure helper virus and because the sequence of28S
RNA remains conserved when propagated with different helper viruses
[8.9.10.11 ]. Hybridization with DNAs complementary to avian tumor
virus RNAs (cDNAs) have distinguished two sets of sequences in each
RNA. One set comprises 60% of the RNA which is related to other,
independently replicating members of the avian tumor virus group
including nondefective Rous sarcoma virus ( ndRSV) [8-11 ]. This
set is termed group-specific and probably represents defective replicative
genes as well as conserved regulatory and structural elements [8,9,
10]. The second set com prises the specific sequences of MC29 and
MH2 RNA. which represent 40% of each RNA and is a likely candidate
for the onc gene of these viruses. Since neither MC29 nor MH2 RNA
contains sequences related to the onc gene of ndRSV, which is termed
src. it has been suggested that these viruses contain distinct onc
genes [8-11]. These and similar studies on avian [9-15] and murine
[16-18,23] viruses have suggested that within a given RNA tumor
virus family, transforming genes may differ whereas replicative
genes are relatively conserved. It is the purpose of this study
to biochemically define the onc genes of MC29 and MH2 in order to
structurally and functionally compare them to each other and to
the src gene of RSV. The src gene of ndRSV has been unambiguously
defined by analyses of src-deletion mutants and srcrecombinants
as a sequence of about 1500 nucleotides that segregates with sarcomagenicity
[ 13. 15.19]. Moreover the src gene was mapped near the 3' end of
viral RNA [14.15, 19] and appears to be translated into a protein
of 60000 daltons [20.21]. Due to their defectiveness in all three
replicative genes [4.5.6] onc-deletion mutants and recombinants
of MC29 and MH2 would lack biologically detectable genetic markers
in replicative genes. Further. the specific sequences of MC29 are
not expected to recombine readily with other avian tumor viruses
lacking them, because analysis of tumor virus recombination has
demonstrated that efficient recombination only occurs between closely
related, allelic sequences [22]. Therefore, the approach that was
used to define src ofndRSV cannot yet be used to define the onc
genes of MC29 and MH2 or to define the onc genes of other defective
transforming viruses. In this paper we describe an alternate, more
biochemical, approach to the definition of the onc genes of MC29
and MH2. We identify (for MC29 and MH2) and locate ( only for MC29)
on the viral 28S RNAs strain-specific and group-specific sequences,
we then investigate, in the case of MC29, the proteins encoded by
these sequences with an interest in identifying a protein involved
in cell transformation. Preliminary work has been described [9-1l]
and recently a more complete comparison of MH2 and MC29 has been
published [40].
Results
MC29 and M H2 Contain Specific 28S RNA Species which Share Specific
Oligonucleotides
A 28S RNA species that is physically and chemically distinct from
the 34S RNA of the helper virus has been found in several defectjve
virus-helper virus complexes of MC29 and of MH2 [8-11]. To demonstrate
that the 28S RNA species in each virus complex was specific to the
defective transforming MC29 or MH2 virus, different MC29 and MH2
pseudotypes have been investigated for the presence of28S RNAs.
It can be seen in Fig. 1 that three different MC29 pseudotypes,
MC29 (ring-neck pheasant virus [RPV]), MC29 (MC-associated virus
of subgroup A [MCA V-A]) and MC29 (MCA V-B) each contained a 28S
RNA species in addition to the 34S RNA of the respective helper
virus. The same was true for the MH2 pseudotypes, MH2 (MH2AV of
subgroups A and C [A+C]) and MH2 (RAV-7) (Fig.l). By contrast, the
RNA of helper viruses RPV [8], MCA V-A, MH2A V-A + C and RA V- 7
contained only a 34S RNA species (not shown). It was concluded that
different pseudotypes of MC29 as well as of MH2 each share physically
indistinguishable 28S RNA species. We have investigated the large
RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of the 28S RNAs of MC29 and
MH2 as specific diagnostic markers of each viral RNA. This is experimentally
complicated because owing to their defectiveness these viruses only
replicate in the presence of a helper virus. Hence viral RNA is
a mixture of defective and helper virus RNAs, the ratio of which
may vary with a given infected culture [8]. If28S RNA is present
at equal or higher concentration than 34S RNA in this mixture, it
can be detected and v isolated by preparative electrophoresis as
is shown in Fig. 1. However, 28S RNA prepared in this fashion is
still contaminated by degraded 34S RNA, the degree of contamination
depending on the relative amount of 34S RNA present in the mixture
and on the integrity of each RNA species.
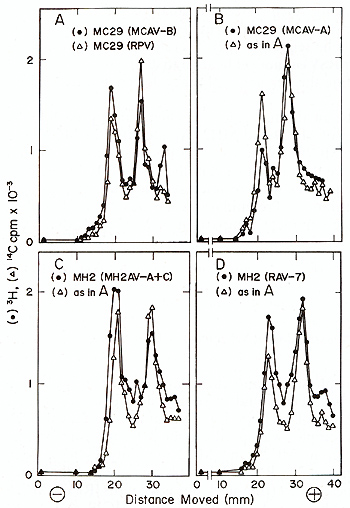
Fig. 1. The RNA monomers of different avian acute
leukemia virus MC29-pseudotypes and of different avian carcinoma
virus MH2-pseudotypes after electrophoresis in 2% polyacrylamide
gels. Preparation of viral RNA and conditions for electrophoresis
have been described [8]. Each RNA was electrophoresed with MC29
(ring-neck pheasant virus of subgroup F [RPV]) RNA standards containing
a 28S MC29 and a 34S RPV RNA species [8]. (A) RNA of MC29 (MCA V-B).
This pseudotype of MC29 was propagated on chick embryo fibroblasts
and was obtained from C. Moscovici, who had received it via R. Smith
from J. Beard. (B) RNA of MC29 (MCA V-A). This pseudotype of' MC29
was also propagated on chicken fibroblasts and was obtained from
C. Moscovici, who had received it from K. Bister and P. K. Vogt.
(C) RNAs of MH2 (MH2A V-A and C) and (0) of MH2 (RA V- 7). These
pseudotypes of MH2 were prepared by one of us (P. K. Vogt) and had
been propagated on chicken macrophage cultures
Degraded 34S RNA that has the size of 28S RNA would coelectrophorese
with intact 28S RNA of MC29 or MH2. Thus in order to distinguish
28S RNA-specific oligonucleotides from oligonucleotides derived
from fragmented 34S RNA present in a given pool of 28S RNA, we have
fingerprinted both RNA species. By subtracting from the 28S RNA
oligonucleotides that the 34S and 28S RNAs have in common, we arrived
at a minimal estimate of 28S RNAspecific oligonucleotides. A complete
catalogue of 28S RNA-specific oligonucleotides must also identify
those oligonucleotides that the 28S RNA of a defective virus may
have in common with the 34S helper virus RNA. Determination of such
oligonucleotides was approached by analyses of 28S RNA pools that
are little contaminated by 34S RNA (as was the case for RNA from
MC29 (RPV) propagated by the quail Q8-cell line [8]) or by identifying
specific oligonucleotides from different 28S RNA pools ofa given
defective virus that was propagated with different helper viruses.
Fingerprint analysis of 28S MC29 RNA prepared from MC29 (RPV) is
shown in Fig.2A and that of 34S RPV RNA has been published previously
[8]. A comparison indicates that of all the T1-oligonucleotides
numbered in Fig.2A, 28S MC29 RNA shares three, i. e., nos. 4,9 and
C with RPV RNA (8,9, Table I). Since the relative concentration
of no.4 was lower than that of all others in Fig.2A and varied with
different preparations of 28S MC29 RNA, we conclude that it was
derived from contaminating RPV RNA (therefore it is in parentheses
in Fig.2A). Henceforth, the oligonucleotides of 28S RNA pools that
are thought to derive from contaminating helper virus RNA are parenthesized
in the Figures and Tables. Oligonucleotides shared with helper viruses
that are present at equimolar ratios are believed to be integral
parts of the 28S MC29 RNA shown in Fig. 2A. This was directly proven
in the case of oligonucleotide no.9. This oligonucleotide is a conserved
element of the gag gene of other avian tumor viruses. which maps
near the 5' end of viral RNAs [27,28]. If this oligonucleotide were
present in a 28S RNA pool of MC29 (RPV) RNA as part of a RPV fragment,
this fragment would have to include the 5'end of the 34S RNA but
would lack the 3' poly(A) end. Therefore only the poly(A)-tagged
species of a 28S RNA pool of MC29 (RPV) RNA had been fingerprinted
in Fig.2A. The result that oligonucleotide no.9 was present indicates
that it was an integral part of28S MC29 RNA. Its presence at a slightly
lower than equimolar concentration in poly(A)-selected 28S RNA (Fig.2A)
was expected, because the 5' end of the RNA would be preferentially
lost in a poly(A) selection (compare Figs.2A and 3A below). Analyses
of the RNase A-resistant fragments of the large T l-oligonucleotides
of the 28S and the 34S RNA species of MC29 (MCA V-B) shown in Figs.2B
and C have not yet been completed. Preliminary results indicate
that the 28S RNA species share several, large oligonucleotides with
28S MC29 RNA isolated from MC29 (RPV). These homologous oligonucleotides
were given the same numbers in Fig.2A and B. In addition, the 28S
RNA species of MC29 (MCA V-B) contained oligonucleotides which appeared
to have chromatographic counterparts in the 34S helper virus RNA
of MC29 (MCA V-B) shown in Fig.2C. Some of these probably derived
from contaminating 34S helper RNA. In addition 28S MC29 RNA may
also have acquired some helper viral oligonucleotides by recombination.
To identify MH2 RNA-specific oligonucleotides, 28S RNA pools from
MH2 (MH2A V-A and C) and from MH2 (RA V- 7) were compared to each
other and to those of their 34S helper virus RNAs (Fig.2E-H) as
described above for MC29 RNA. MH2-specific oligonucleotides are
numbered without parentheses in Fig. 2E, F and Table 2. Further
work is necessary to determine whether some of the oligonucleotides
shared by 28S MH2 and 34S MH2A V
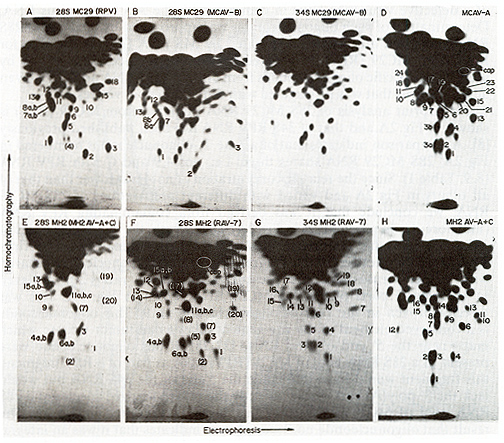
Fig.2. Autoradiographs of RNase T1-digested viral [32P]
RNA compOnents after 2-dimensional electrophoresis-homo-ehromatography
(fingerprinting). Preparation of viral RNA components and conditions
of fingerprinting have been described [8.14]. Numbers identify large
RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides. or sp ots co)nsisting of more
than one oligonucleotide. L " " Numbers ofoligonucleotides of28S
RNA pools which are probably derived from degraded 34S helper virus
RNA are parenthesized. Cap designates the 5' terminal capped oligonucleotide.
The following RNAs were fingerprinted: (A) The poly(A)-containing
28S MC29 RNA prepared electrophoretically from MC29 (RPV) RNA as
in Fig. land chromatographed on oligo(dT)-cellulose [141. (8) the
28S RNA of MC29 (MCAV-8). electrophoretically prepared from MC29
(MCA V-8) RNA as for Fig. I. (C) the 34S MCA V-8 RNA electrophoretically
prepared from MC29 (MCA V-8) as in (8). (0) the 60-70S RNA of MCA
V-A prepared from virus propagated in chicken fibroblasts. (E) the
28S RNA ofMH2 (MH2A V-A and C). prepared as for (A.8). (F) the 28S
RNA of MH2 (RAV-7) also prepared as for (A.8). (G) the 34S RAV-7
RNA prepared from MH2 (RA V-7) RNA as described for (C) and (H)
the 50-70S RNA of MH2A V-A and C. A mixture of these two helper
viruses was propagated in chicken fibroblasts
A and C or 34S RA v- 7 RNAs are integral parts of 28S MH2 RNA or
are derived from degraded helper virus RNA. Analysis of 28S RNA
was hampered by difficulties with propagating sufficient radioactive
virus in chicken macrophages [5] for biochemical analyses of RNA
and because virus from transformed chicken or quail fibroblast cultures
contained. in over thirty cases tested, > 3 times more 34S than
28S RNA, and was thus unsuitable for studying 28S RNA.
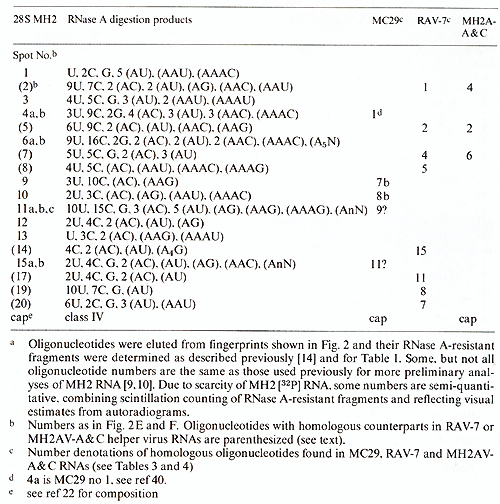
Table I. Composition of T1-oligonucleotides
of 28S MC29 RNAa
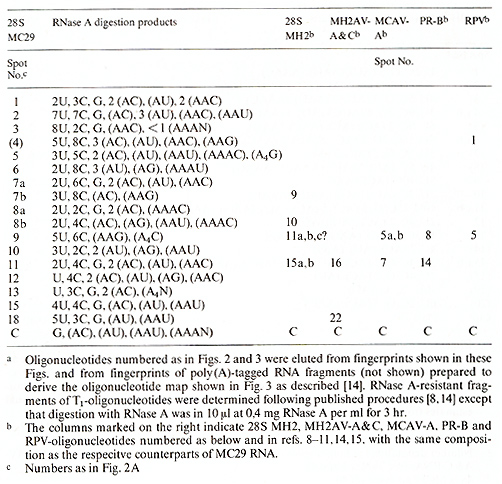
A comparison of the oligonucleotides of 28S MC29 and MH2 RNAs indicates
that the two RNAs share about 5 out of 12-15 large oligonucleotides
(see Tables 1 and 2). Three of these common oligonucleotides are
also shared with other avian tumor viruses. However two are only
shared by MC29 and MH2. i. e., nos.7b and 8b of MC29 and nos.9 and
10 of MH2. Hence it is conceivable that these oligonucleotides are
part of the functionally related, specific onc genes of these two
viruses. It has been argued that (defective) transforming viruses
are generated by recom bination of a helper virus with an unknown
( defective) virus preexisting in the cell or with cellular genetic
elements [ 16-18,23,24]. The helper viruses isolated from the original
stocks of MC29 and MH2 would appear to be likely candidates for
one parent of such recombinational events. It would then be expected
that the defective recombinant virus shares more sequences with
its progenitor than with other possible helper viruses. To test
this, the RNA ofa cloned helper, isolated from the original MC29
stock, i. e.,
Table 2. T1-oligonucleotides of 28S MH2
RNAa
MCA V-A. was fingerprinted (Fig.2D) and the RNase-A resistant fragments
oflarge oligonucleotides were compared to those of28S MC29 RNA isolated
from MC29 (RPV). It can be seen in Tables 1 and 3 and Fig.2 that
the two RNAs share only about three of their large T1-oligonucleotides.
In addition both RNAs as well as RPV RNA have the same 5' terminal
capoligonucleotide (marked in Fig. 1) [22]. The same was true for
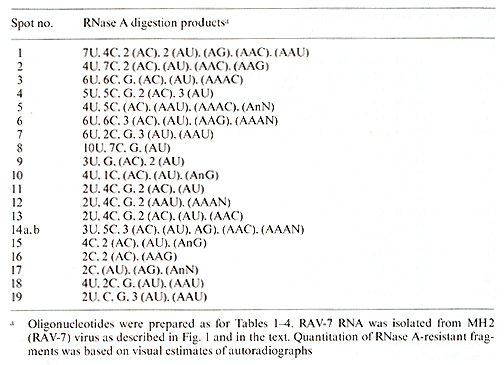
the relationship of 28S MH2 RNA to MH2A V-A and C RNAs, two helper
viruses isolated from the original stock of the virus. These helper
viruses did not share more oligonucleotides with MH2 RNA than with
RA V-7 (compare Fig.2 and Tables 2, 4 and 5). We conclude on the
basis of oligonucleotide homologies. that 28S MC29 and MH2 RNAs
are not more closely related to their original helper viruses than
to the other helper viruses tested.
Table 3. Composition of T1-oligonucleotides
of MCAV-A RNAa
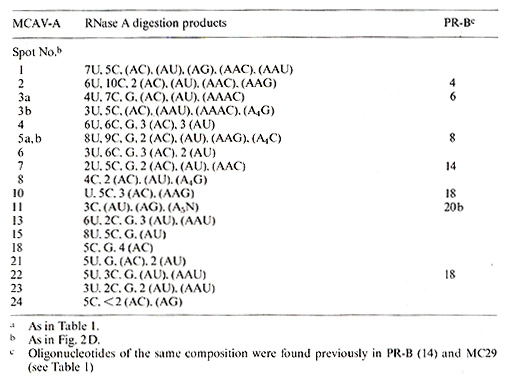
Table 4. Composition of T1-oligonucleotides of MH2AV-A
and -C RNAa

Table 5. T1-oligonucleotides of RAV- 7 RNA
The Relationship of28S MC29 and MH2 RNAs to Each Other and to the
RNAs ofOther Avian Tumor Viruses Measured by Hybridization
To determine whether 28S MC29 and 28S MH2 RNA contain src-specific
nucleotide sequences of avian sarcoma viruses and to investigate
their relationship to each other and to the RNAs of helper-independent
avian RNA tumor viruses. the RNAs were hybridized to various cDNAs.
All hybridizations were carried out with an excess ofcDNA and at
increasing cDNA to RNA ratios to reach plateau values of maximal
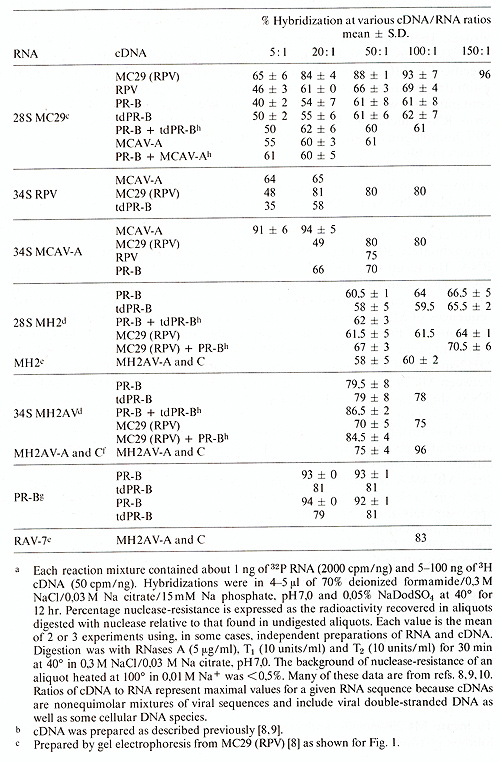
hybridization. Under our conditions. maximal hybridization of 28S
MC29 RNA with homologous MC29 (RPV) cDNA and of Prague RSV-E (PR-E)
RNA with homologous cDNA was about 93% (Table 6). To determine whether
28S MC29 and MH2 RNAs contain src-specific sequences each RNA was
first hybridized to cDNA from PR-E which contains src and then to
cDNA from transformation-defective (td) PR-E which lacks src [13-15].
It is seen in Table 6 that approximately the same percentage (62
to 66%) of each RNA was hybridized by each cDNA. The MC29 and MH2
RNA sequences hybridized bv PR-B and td PR-B cDNA were not additive,
because a mixture of these two cDNAs did not hybridize more than
each by itself (Table 6). The PR-B cDNA used was shown to include
.s'rc-specific sequences. because it was able to hybridize 13% more
PR-B RNA than td PR-E cDNA (Table 6). This was the expected difference.
because the .src gene corresponds to about 13% of the viral RNA
[ 13]. It follows that MC29 RNA and MH2 RNA lack src-specific sequences.
About 62 to 66% of MC29 and MH2 RNAs are related to the RNAs of
PR-B, td PR-E and other independently replicating avian tumor viruses.
Therefore these sequences are termed group-specific. At least 31
% (i. e.. 93 minus 62) or 1700 nucleotides of each RNA would appear
to be specific for MC29 or MH2, respectively. This is considered
a minimal estimate because each electrophoretically prepared 28S
RNA was contaminated with degraded helper virus RNA ( c. f., Figs.
land 2). Helper virus RNAs including RPV RNA, 34S MH2A V-A and C
RNA were 60 to 80% homologous to the RNAs of PR-E, td PR-B and of
other avian tumor viruses (Table 6). To test whether the specific
sequences of MC29 and MH2 RNA (defined as those which did not hybridize
with PR-B or td PR-E cDNA) are related to each other, 28S MH2 RNA
was hybridized to MC29 (RPV) cDNA. About 64% of the RNA was hybridized
(Table 6). Ifannealed with MC29 (RPV) and PR-B cDNAs, about 70%
of 28S MH2 was hybridized. It follows that approximately 30% of
the 28S MH2 RNA is unrelated to MC29 and PR-E RNA. The result that
about 5-10% more 28S MH2 RNA was hybridized by MC29 (RPV) and PR-B
cDNAs together than by each cDNA alone, may indicate that each of
these cDNAs contains sequences related to different sequences of
MH2. It is conceivable that PR-B cDNA would hybridize with segments
of the above defined group-specific sequences of MH2 not represented
in MC29 (RPV) cDNA and MC29 cDNA with segments of MH2-specific RNA
not represented by PR-B cDNA. A specific relationship between MC29
and MH2 is consistent with the finding that MH2 and MC29 RNAs share
two oligonucleotides not found in any other avian tumor virus tested
here (see above). To test further the notion mentioned above that
defective transforming viruses are recombinants of a helper virus
and an unknown parent, sequence homologies between the RNAs of MC29
and of its original helper virus. MCA V-A as well of MH2 and of
MH2A V-A and C were determined. It is seen in Table 6 that 28S MC29
RNA is hybridized by MCA V-A cDNA to approximately the same extent,
i. e., 61 %, as by cDNA prepared from other avian tumor viruses.
The same was true for 28S MH2 RNA and MH2A V-A and C cDNA (Table
6). The MCA V-A cDNA as well as the MH2A V-A and -C cDNA used, hybridized
94-96% of their homologous viral RNAs (Table 6). It is concluded
that MC29 and MH2 are not more closely related to their original
helper viruses than to other avian tumor viruses tested. This conclusion
is consistent with the results described above that the T 1oligonucleotides
of MC29 and MCA V-A as well as those of MH2 and MH2A V-A and C RNAs
are not more closely related to each other than to those of other
avian tumor virus RNAs.
Table.6. Hybridization a of viral RNAs
with viral cDNAs b
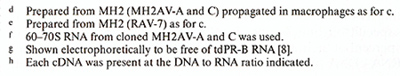
Mapping MC29-Specific and Group-Specific Sequences ofMC29 RNA
To locate MC29-specific and group-specific sequences on MC29 RNA the
following strategy was used: First the RNase T 1-resistant oligonucleotides
of the MC29-specific and of the group-specific segments of MC29 RNA
were determined. MC29-specific RNA segments were recovered from RNA-DNA
hybrids formed between viral RNA and MC29-specific cDNA. Group-specific
segments of MC29 RNA were obtained from hybrids formed with cDNAs
from other avian tumor viruses [10,11,26]. The location of the RNA
segment to which a given oligonucleotide belonged was then deduced
from a map of all large oligonucleotides of MC29 RNA. An oligonucleotide
map describes the location of each large oligonucleotide relative
to the 3' poly(A)-coordinate ofviral RNA. The location ofa given oligonucleotide
is deduced from the size of the smallest poly(A)-tagged RNA fragment
from which the oligonucleotide can be obtained [ 14]. MC29-specific
cDNA was prepared by hybridizing MC29 (RPV) cDNA to an excess of unlabeled
RNA of RPV and of PR-E under conditions of moderate stringency (Fig.
3). In this way all but the MC29-specific sequences of this cDNA were
converted to heteroduplexes leaving only MC29-specific cDNA single-stranded.
This cDNA was then hybridized in a second step with 50--70S MC29 (RPV)
[32P] RNA essentially under the conditions described above. However
incubation was for a shorter time, to minimize displacement of unlabeled
RNA from heteroduplexes present in our preparation ofMC29specific
cDNA by related or identical sequences of MC29 [32P] RNA. After digestion
of unhybridized MC29 (RPV) [32P] RNA with RNases A and T1, the resulting
hybrids were prepared by chromatography on Eiogel P1OO. Subsequently
the hybrid was heat-dissociated and the [32P] RNA was digested with
RNase T 1. The resulting MC29-specific T 1-o1igonucleotides were detected
by fingerprint analysis (Fig. 3E) and their RNase A-resistant fragments
were determined (Table I). The remaining oligonucleotides of MC29
RNA (Fig. 3A) are expected to derive from group-specific RNA segments,
sequence-related to the RNAs of other members of the avian tumor virus
group. Group-specific RNA sequences were identified as follows: 28
S MC29 [32P] RNA was prepared electrophoretically from 50-70S MC29
(RPV) RNA [8]. The RNA was then hybridized to an excess of PR-B and
RPV cDNA as above (Fig. 3 C). After hybridization the reaction mixture
was treated with RNase T 1 to degrade unhybridized RNA. RNase A was
not used for this purpose in order to preserve small MC29-specific
oligonucleotide segments which are part oflarger group-specific polynucleotide
segments of MC29 RNA hybridized with PR-E and RPV cDNAs. Thus mismatches
involving oligonucleotide segments with fewer than two Gs would register
as complete hybrids in our conditions. Such mismatches are expected
because neither RPV nor PR-E are immediate predecessors of MC29 and
because group-specific sequences of avian tumor virus RNAs defined
by hybridization are known to differ if compared by
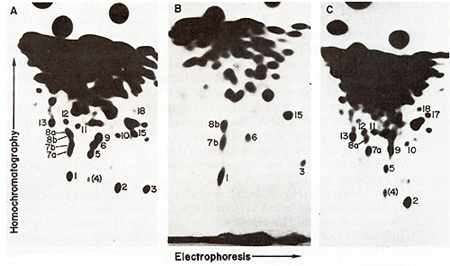
Fig.3. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of whole 28S
MC29 RNA (A). of MC29 RNA sequences that are not sequence-related
to other avian tumor virus RNAs ( MC29-specific) (8). and of MC29
RNA sequences that arc sequence-related to other avian tumor virus
RNAs (group-specific) (C). 28S MC29 [32P] RNA was prepared clectrophoretically
from 50 70S MC29 (RPV) RNA. digested with RNase TI and subjected
to 2-dimensional electrophoresis-homochromatography as described
[8.14]. Oligonucleotides were numbered as in rig. 2 and previousIv
[8-11]. In cases where double-spots were resolved. distinct oligonucleotides
were denoted alphabetically (Fig. 2. Table I ). Oligonucleotide
no.4 is in parenthesis because it is thought to derive from contaminating
RPV RNA [8] rather than from MC29 RNA (see Fig. 2). (8) To prepare
MC29-specific sequences from MC29 RNA. 50-70S MC29 (RPV) [32P] RNA
was hybridized to MC29-specific cDNA. MC29-specific cDNA was made
by incubating 2 µg MC29 (RPV) cDNA [8.19] with 15 µg RPV RNA and
12 µg PR-8 RNA for 12 hr at 40OC in 10 µI 50% formamide containing
0.45 M NaCl. 0.045 M Na citrate and 0.01 M Na-PO4 pH7.0. Subsequently.
1.5 µg of MC29 (RPV) 32p] RNA (5 x 10 high 6cpm/µg) was added in
20 µI of the above formamide buffer and incubation was continued
for I hr. After digestion for 30 min at 40OC in 200 µI of 0,3 M
NaCI, 0,03 M Na citrate containing 5 µg/ml RNase A and 50 units/mI
RNase TI, the resistant hybrid was isolated from the void volume
of a Biogel P lOO column (12xO,6 cm) equilibrated in 0,1 M NaCl,
0,01 M Tris pH7,4, 1 mM EDTA and 0,2% Na dodecylsulfate. Hybrid
was extracted 3 times with phenol in the presence of 30 µg carrier
yeast tRNA, then ethanol-precipitated, heat-dissociated in buffer
of low ionic strength, digested with RNase T I and subjected to
fingerprint analysis as above. The oligonucleotides from MC29-specific
RNA segments so identified are underlined in the oligonucleotide
map shown in Fig. 4. (C~) To prepare avian tumor virus group-specific
sequences of MC29 RNA, 0,25 µg of electrophoretically prepared 28
S MC29 [32P] RNA (Fig. I, refs. 8,9,10) (2 X 10 high 6 cpm/µg) was
hybridized with I µg of PR-8 and 1 µg of RPV cDNAs for 12 hr in
25 µI of 70% formamide, 0,3 M NaCl- 0,03 M Na citrate. 0,02% Na
dodecylsulfate and 0,015M Na-P04 pH7,0. The reaction product was
heated to 50OC for 1 min in 0,15 M NaCl, 0,015 Na citrate pH7,0
and treated with RNase TI (but not with RNase A) and otherwise as
described for (B)
fingerprinting T1-o1igonucleotides [14, 15,27,28]. This is because
fingerprinting detects specific oligonucleotides even in RNA sequences
which differ by only a few percent of their nucleotides and which
are closely related if compared by RNA-cDNA hybridization. The T1-oligonucleotides
of the result ing hybrid are shown in Fig. 3C and Table 1. They
represent RNA sequences of MC29 RNA that are closely related to
but not identical with sequences of PR-B and RPV RNA. It can be
seen in Figs. 3 and 4 that the T 1-o1igonucleotides of MC29 RNA
fall into two non-overlapping sets. those representing MC29specific
and those representing group-specific sequences of MC29 RNA. An
oligonucleotide map of 28 S MC29 [32P] RNA was derived by fingerprinting
poly(A)-tagged fragments of electrophoretically purified 28 S MC29
RNA (Fig.4). The approximate distance of each large oligonucleotide.
numbered as in Figs. 2 and 3, is given in nucleotides as well as
in relative map units. each originating at the 3' poly (A) coordinate.
The specific oligonucleotides (underlined in Fig. 4) mapped together
between 0,4 and 0,7 units with some uncertainty about the relative
order of nos. 2 and 8 b. Oligonucleotides of group-specific sequences
(not underlined) are found at the 5' end and in the 3' half of viral
RNA. The group-specific sequences of the 5' end included oligonucleotide
no.9. previously identified as a conserved element of the gag gene
of other avian tumor viruses (see above ) [27.28]. The 3' half contained
oligonucleotide no.11 , found previously at the src border ofenv
in other virus RNAs [14, 15,27,28] and the highly conserved C oligonucleotide
which maps near the 3' end of avian tumor virus RNAs [14].
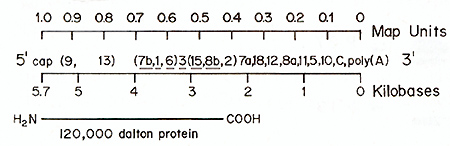
Fig.4. Oligonucleotide map of 285 MC29 RNA. 28S MC29
[.32P] RNA (approx. 6 X 106 cpm) was prepared electrophoretically
from 50-705 MC29 (RPV) RNA. The RNA was degraded by incubating 3
equal aliquots for 3.6 and 9 min. respectively. in 0.05 M Na2CO.3
at pH 11.0 and 50°C. Fragments were combined and poly(A)-tagged
species selected on oligo(dT)-cellulose and fractionated into different
size classes as described [14]. The T1-o1igonucleotides of 6 size
classes of RNA fragments differing by approximately 1000 nucleotides
from each other. were fingerprinted (not shown). Oligonucleotides
of fragment,; were identified by their chromatographic properties
and by their RNase A-resistant fragments (Table 1). and are numbered
as in Fig. 2.3 and Table I. The resulting order of oligonucleotides
is plotted on 2 scales. one denoting the approximate distance of
an oligonucleotide from the 3' poly(A)-coordinate in kilohases.
the other denoting it in relative map units. When the relative order
of oligonucleotides was uncertain. they are shown in brackets. Oligonucleotides
from strain-specific sequences ofMC29 RNA (Fig. I B) are underlined
and those from group-sequences (Fig. I C) are not underlined. The
bottom line represents the MC29-specific. 120000 dalton protein
P 120mc. It is drawn in a position that is colinear with the RNA
segment from which it was probably translated based on data described
in the text and previously (10.11)
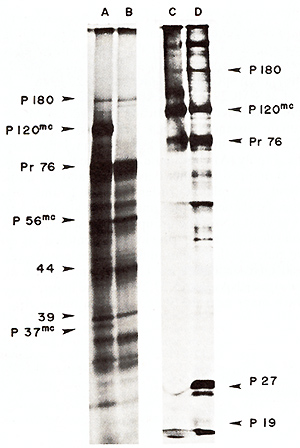
Fig.5. Electrophoretic analysis ofin vitro translation
products ofviral RNAs. RNAs were translated in the messenger-dependent
rabbit reticulocyte lysate. [35S]-methionine was present at 400
µCi/ml (600-1200 Ci/mmol). Products were analyzed by electrophoresis
on a 12.5% polyacrylamide slab gel. The gel was autoradiographed
after fixing and drying [4.10.11 ]. Tracks A and B show the products
of total heat-denatured. poly(A)-selected ( 14) 50-70S virion RNAs
from MC29 (RPV) and RPV (Track A). and from RPV alone (Track B).
Track C shows the cellfree translation-products of MC29 (RPV and
RPV RNA (as in Track A). and Track D shows the proteins precipitated
with antibody to disrupted avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV (which
contains mainly antibody to gag protein) from MC29 (RPV infected
cells. Immunoprecipitations were carried out as described [4.20].
The viral proteins precipitated by anti-AMV serum were not precipitated
by control serum. and P 120mc was not synthesized in RPV-infected
cells (not shown)
In Vitro Translation of MC29 RNA
To identify the products of the MC29 RNA genome, the RNA was translated
in a cell-free system. Using this technique it has been possible
to identify the ,gag, pol, src, and possibly also the env gene products
of RSV[21,29,30,31].MC29 (RPV) 50-70S RNAs were heat-denatured,
poly (A)-selected, and translated in the messenger-dependent rabbit
reticulocyte lysate [ 10, II]. Products were analyzed by polyacrylamide
gel electrophoresis. To identify the products specified by the MC29
RNA, the products of total poly (A)-selected MC29 (RPV) RNAs (Fig.5,
track A) were compared with those of RPV RNA alone (Fig. 5, track
B). A number of products were in common between the two tracks,
and these were assumed to be products of the RPV RNA. These include
a 180000 dalton-molecular weight polypeptide (P 180), which is believed
to be the gag-pol gene product [31]; Pr76, the primary product of
the gag gene [30,31 ,32] and a number of smaller products, most
of which are immunoprecipitated by antiserum to the gag protein,
P27, and were only synthesized from full-length 34S RNA, suggesting
that they are premature termination products of the gag gene [II].
In addition to these products there were three polypeptides which
are specific to MC29 RNA. They have molecular weights of 120000,56000,
and 37000 daltons on this gel system, and will be denoted as P 120mc,
P56mc, and P37mc (Fig. 5). P 120mc was a major product of the MC29
(RPV) RNA mixture, and was synthesized with the same order of efficiency
as Pr76 (since they have a similar number of methionine residues
[11]). A protein of similar size was recently found in MC29-infected
cells and was shown to contain serological determinants of the viral
gag gene proteins [4 ]. To test the relationship of the two proteins,
P 120mc was compared electrophoretically to its presumed counterpart
precipitated from MC29-infected cells with antibody to disrupted
avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV, which includes antibody to gag
proteins. It can be seen that both proteins were electrophoretically
identical (Fig. 5 C, D). In addition P 120mc synthesized in vitro
was specifically immunoprecipitated by antiserum to P27 of AMV,
the major gag gene protein, indicating that it contains determinants
of gag proteins (not shown). P 120mc was not recognized by antisera
against products of the pol and env genes (not shown). Further evidence
that the in vivo and in vitro-made P120mc are the same has been
obtained recently [11]. We conclude that the P120mc translated in
vitro from viral RNA and that found in MC29-infected cells are probably
the same and that P 120mc contains gag-related and MC29-specific
peptides.
Discussion
The RNA and Gene Products of MC29 and MH2
The finding that different pseudotypes of MC29 or MH2 contained
physically and chemically very similar or identical 28 S RNAs, but
34S RNAs that varied with the respective helper virus, proved that
the 28 S RNAs are MC29or MH2-specific. Each 28 S RNA contained 30-40%
of specific nucleotide sequences, which only hybridized with homologous
cDNAs and 60-70% of sequences which hybridized with cDNAs ofother
avian tumor viruses which were termed group-specific. Src gene-related
sequences were not detected in 28S MC29 or MH2 RNA.
In the case of 28 S MC29 RNA, the specific sequences, identified
by the large T1-oligonucleotides they contain, mapped about 0,4
to 0,7 map units from the poly (A) end of the RNA (Fig. 4). The
observation that MC29 and MH2 share two specific oligonucleotides,
which in MC29 RNA mapped in a contiguous, MC29-specific RNA segment
(Fig. 4), suggests that the specific sequences of the two viruses
are related. This relationship has since been extended to three
oligonucleotides [ see Table 2 and ref40]. In vitro translation
of MC29 RNA generated one major 120000 dalton protein product. and
two minor proteins of 56000 and 37000 daltons. The 120000 MC29 protein
included protein sequences serologically related to the gag gene
of other avian tumor viruses. Since one gag gene-related oligonucleotide.
i.e.. no.9. was found near the 5' end of MC29 RNA and since the
gag gene of other avian tumor viruses maps near the 5' end of their
RNAs [27.28] it appears plausible that the gag gene-related portion
of the 120000 MC29 protein was translated from the 5' end of the
RNA and that the remainder was translated from the MC29-specific
sequences of the viral RNA (Fig. 4). Our recent observation that
only full-length 28 S MC29 RNA can be translated into P 120mc [
11] also argues for a 5' map location of this protein. because eukaryotic
mRNAs only effectively use one initiation site near the 5' terminus
[33.34.35]. The group-specific sequences that MC29. MH2 and other
avian tumor viruses have in common are nearly indistinguishable.
If compared by hybridization. but are distinct in each viral RNA
if analyzed by the more sensitive method of fingerprinting. which
detects single base changes. Since MH2 and MC29 do not express replicative
genes, we can only speculate on the function of the group-specific
sequences of their RNAs. Some of these sequences must play direct
roles in virus replication by providing specific sites for packaging
of viral RNA into helper virus proteins, for reverse transcription
of viral RNA and for diller linkage of 28S RNA monomers [6,8,9.10].
The gagrelated, group-specific sequences of MC29 are translated
into P 120mc and mayas such be involved in transformation (see below).
Further analyses of P56mc and P37mc are necessary to determine whether
their sequences overlap with P 120mc or with each other or whether
they correspond to distinct segments of viral RNA. since MC29 RNA
may code for approximately 200000 daltons ofprotein.
What is the Onc Gene of MC29 and MH2?
Since neither MC29 nor MH2 contain src gene-related sequences. there
are two different hypotheses as to which RNA sequences of these
viruses represent their onc genes. One suggests that the specific
sequences constitute the onc gene. while an alternative hypothesis
suggests that their defective replicative genes i.e.. group-specific
sequences function as transforming genes. We prefer the first hypothesis
for several reasons. The idea that specific RNA sequences apparently
unrelated to the replicative genes might be specific onc genes is
proven for RSV [13.14, 15,19] and has also been postulated for defective
murine sarcoma [16.17.18.23.24] and acute leukemia viruses [9.10.36].
The existence of specific sequences in MC29 and MH2. which are related
to each other. but unrelated to the other avian tumor virus RNAs
tested. suggests that these sequences may belong to a family of
related genes. possibly the functionally related [1-5.9.10] onc
genes of MC29 and MH2. A specific onc gene for this class of viruses
also corresponds with the distinct transformed phenotypes of MC29-
or MH2infected fibroblasts. which differ from those of RSV-transformed
cells [1-5.37]. The result that MC29-specific and group-specific
sequences are translated into a specific protein, P120mc.:, and
that the same protein is also found in transformed cells [4] (and
not in large quantity in the virion [unpublished]) suggests that
this protein may be involved in cell transformation. A possibly
analogous non-structural protein of 120000 daltons, that contains
gag-related and specific peptides has been found in cells transformed
by MH2 [5] and by the defective Abelson murine leukemia virus [38].
Further work correlating the specific RNA sequences of MC29 and
MH2 with the specific determinants of their P 1201111.: proteins
is expected to support the hypothesis that this class of protein
may be involved in transformation. Moreover, it is important to
determine whether the 56000 and 37000 molecular weight MC29 proteins
synthesized in vitro are also synthesized and functional in MC29-infected
cells. While a definite answer to the question of whether the specific
sequences of MC29 or MH2 and the P 120111c proteins are involved
in transformation can only be given if genetic variants become available.
our data allow us to conclude that the onc genes and gene products
in different prototypes of the avian tumor virus family, are different.
Thus MC29 and MH2 must transform cells with gene products and possibly
by mechanisms that differ from those of RSV. Our data. that viruses
with specific oncogenicity carry specific onc genes does not exclude
roles for other viral genes. including those of the helper virus.
in determining the oncogenic spectrum of a defective transforming
virus. For example, the oncogenic spectrum of a defective virus
should be greatly influenced by the env gene of its helper virus
which provides the envelope glycoproteins for the defective virus.
Since the cellular receptors for viral envelope glycoproteins differ
greatly among different animals [39] and even among different target
cells of the same animal [25] different helper viruses may deliver
the same onc genes into specific target cells and thus cause a different
form of cancer.
Acknowledgments
We thank Lorrine Chao for her assistance with this work. and j.
Guyden for help with the analysis of MC29 proteins. Pamela Mellon
is a recipient of a NSF Graduate Fellowship and Anthony Pawson of
a Fellowship from the Science Research Council of the United Kingdom.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grants
CA 11426 and CA 19725 from the National Cancer Institute.
References
1. Purchase. H.G.. Burmester. B.R.: In: Diseases of the Poultry.
Hofstad. M.S.. Calnek. B.W.. Helmboldt. C. F.. Reid. W. M.. Yoder.
H.W.. jr. (eds.). 6th ed.. pp.502-567. Iowa State University Press
1972
2. Hanafusa. H.: In: Comprehensive Virology. Fraenkel-Conrat.
H.. Wagner. R. (eds.). Vol. 10. pp. 401-408. New York: Plenum Press
1977
3. Ishizaki. R.. Langlois. A.j.. Chabot j.. Beard. j.W.: .J. Virol.
8,821-827
4. Bister. K.. Hayman. M.j.. Vogt. P. K.: Virology 82,431-448 (1977)
5. Hu. S. S. F.. Moscovici. C.. Vogt. P. K.: Virology ( 1978) 89,162-178
6. Bister. K.. Vogt. P. K.: Virology ( 1978) 88,213-221
7. Baltimore. D.: Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. BioI. 39,1187-1200
( 1975)
8 Duesberg. P. H.. Bister. K.. Vogt. P. K.: Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci.
USA 74,4320--4324 ( 1977)
9. Duesberg. P. H.. Vogt. P. K.. Bister. K.. Troxler. D.. Scolnick.
E. M.: In: Avian RNA Tumor Viruses. Barlati. S.. de Guili-Morghen.
C. (eds.). pp. 95--111. Padua: Piccin Medical Books 1978
10. Duesberg. P.. Mellon. P.. Pawson. T.. Martin. G. S.. Bister.
K.. Vogt. P.: In: 4th ICN-UCLA Symposium on Animal Viruses. Stevens.
J.. Todaro. G.. Fox. F. (eds.) pp. 245-266. Academic Press. 1978
11. Mellon. P.. Pawson. A.. Bister. K.. Martin. G. S.. Duesberg.
P. H.: Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75,5874-5878 ( 1978)
12. Stehelin. D.. Graf T.: Ce1113, 745-750 ( 1978)
13. Lai. M.-C.. Duesberg. P. H.. Horst. J.. Vogt. P. K.: Proc.
Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70,2266-2270 (1973)
14. Wang. L.-H.. Duesberg. P.. Beemon. K.. Vogt. P. K.: J. Virol.
16, 1051 -1070 ( 1975)
15. Wang. L.-H.. Duesberg. P. H.. Mellon. P.. Vogt. P. K.: Proc.
Natl. Acadi. Sci. USA 73, 1073-1077 (1976)
16. Maisel. J.. Klement. V.. Lai. M.-C.. Ostertag. W.. Duesberg.
P. H.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70,3536-3540(1973)
17. Scolnick. E. M.. Goldberg. R.J.. Parks. W. P.: C'old Spring
Harbor Symp. Quant. Bioi. 39, 885-895 (1975)
18. Dina. D.. Beemon. K.. Duesberg. P. H.: Ce119, 299-309 ( 1976)
19. Joho. R. H.. Billeter. M. A.. Weissmann. C.: Proc. Natl. Acad.
Sci. USA 72,4772-4776 ( 1975)
20. Brugge. J. S.. Erikson. R. L.: Nature 269,346-348 ( 1977)
21. Purchio. A.. Erikson. E.. Erikson. R.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA 74,4661-4665 (1977)
22. Wang. L.-H.. Duesberg. P. H.. Robins. T.. Yakota. H.. Vogt.
P. K.. Virology 82, 472-492 (1977)
23. Scolnick. E. M.. Howk. R. S.. Anisowicz. A.. Peebles. P. T..
Scher. C'.T.. Parks. W. P.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72,4650-4654
( 1975)
24. Scolnick. E. M.. Rands. E.. Williams. D.. Parks. W. P.: J.
Virol. 12,458-463 ( 1973)
25. Gazzolo. L.. Moscovici. M.G.. Moscovici. C.: Virology 58,514-525
(1974)
26. Coffin. J. M.. C'hampion. M. A.. Chabot. F.: In: Avian RNA
Tumor Viruses. Barlati. S.. de Guili-Morghen. C. (eds.). pp. 68-87.
Padua: Piccin Medical Books 1978
27. Wang. L.-H.. Galehouse. D.. Mellon. P.. Duesberg. P. H.. Mason.
W. S.. Vogt. P. K.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73,3952-3956 ( 1976)
28. Duesberg. P. H.. Wang. L.-H.. Mellon. P.. Mason. W. S.. Vogt.
P. K.: In: Genetic Manipula tion as it Affects the Cancer Problem.
Schulz. .J.. Brada. Z. (eds.). pp. 161 179. Academic Press. 1977
29. Pawson. T.. Martin. G. S.. Smith. A. E.: J. Virol. 19,950-967
( 1976 )
30. von der Helm. K.. Duesberg. P. H.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA 72,614-618 ( 1975) '
31. Paterson. B.. Marciani. D.. Papas. T.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.
USA 74,4951-4954 ( 1977)
32. Vogt. V.. Eisenman. R.. Diggelmann. H.: J. Mol. BioI. 96,471-493
( 1975)
33. Jacobson. M. F.. Baltimore. D.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
61,77-84 ( 1968)
34. Glanville. N.. Ranki. M.. Morser. J.. Kaariainen. L.. Smith.
A. E.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73,3054-3063 (1976)
35. Baralle. F. E.. Brownlee. G. G.: Nature 274,84-87 ( 1978)
36. Troxler. D. H.. Boiars. J. K.. Parks. W. P.. Scolnick. E.
M.: .J. Virol. 22,361-372 ( 1977)
37. Rover-Pokora. B... Beug. H.. Claviez. M.. Winkhardt. H.-J..
Friis. R.. Graf. T.: Cell 13, 751 .L to 760(1978)
38. Witte. 0. N.. Rosenberg. N.. Paskind. M.. Shields. A.. Baltimore.
D.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. ' USA 75, 2488-2492 ( 1978 )
39. Tooze. J. (ed.): The Molecular Biology of Tumor Viruses. New
York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Cold Spring Harbor 1973
40. Duesberg. P. H. and Vogt. P. K.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
76, 1633-1637 ( 1979)
|